Supercomputing Modelling Final Exam Project. Download the report.
Check out the git repo!
Calculation of Density in the SPH Method
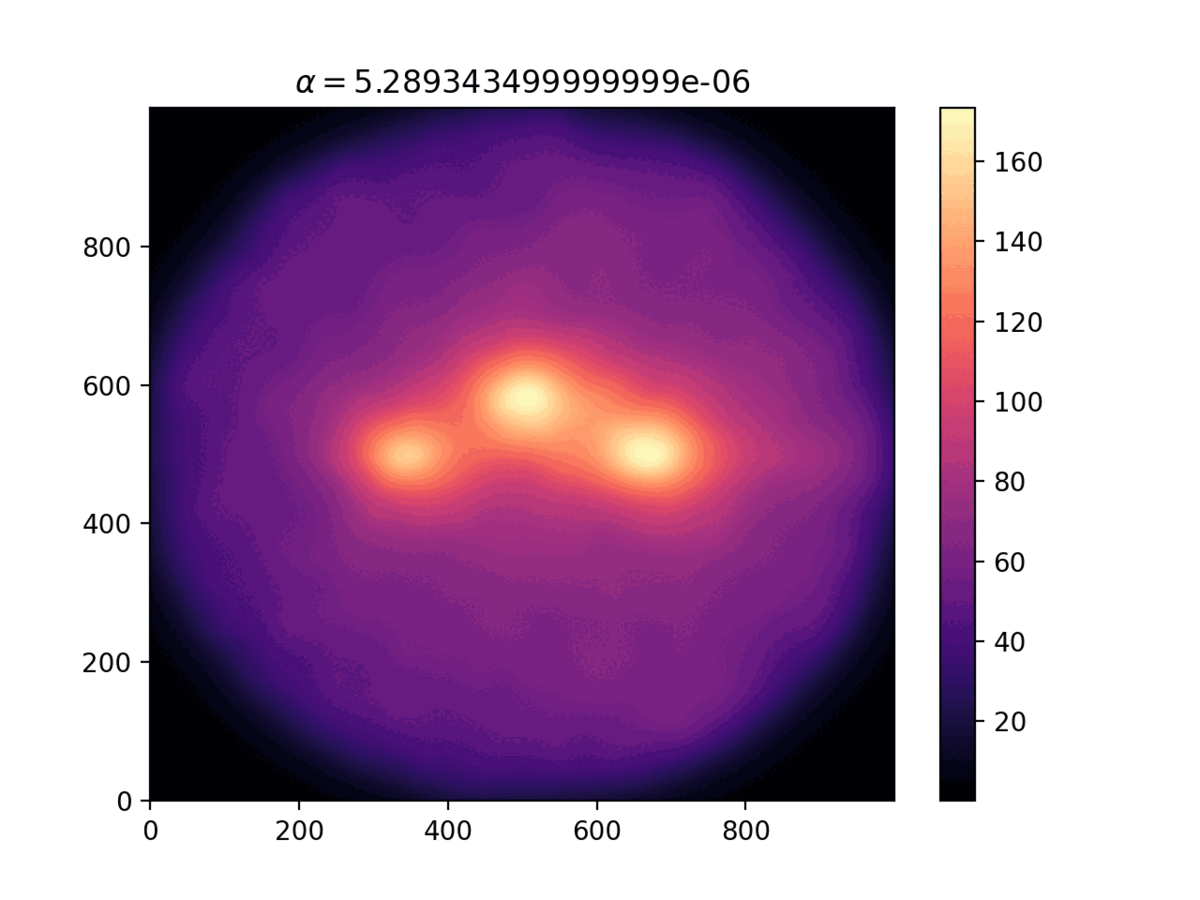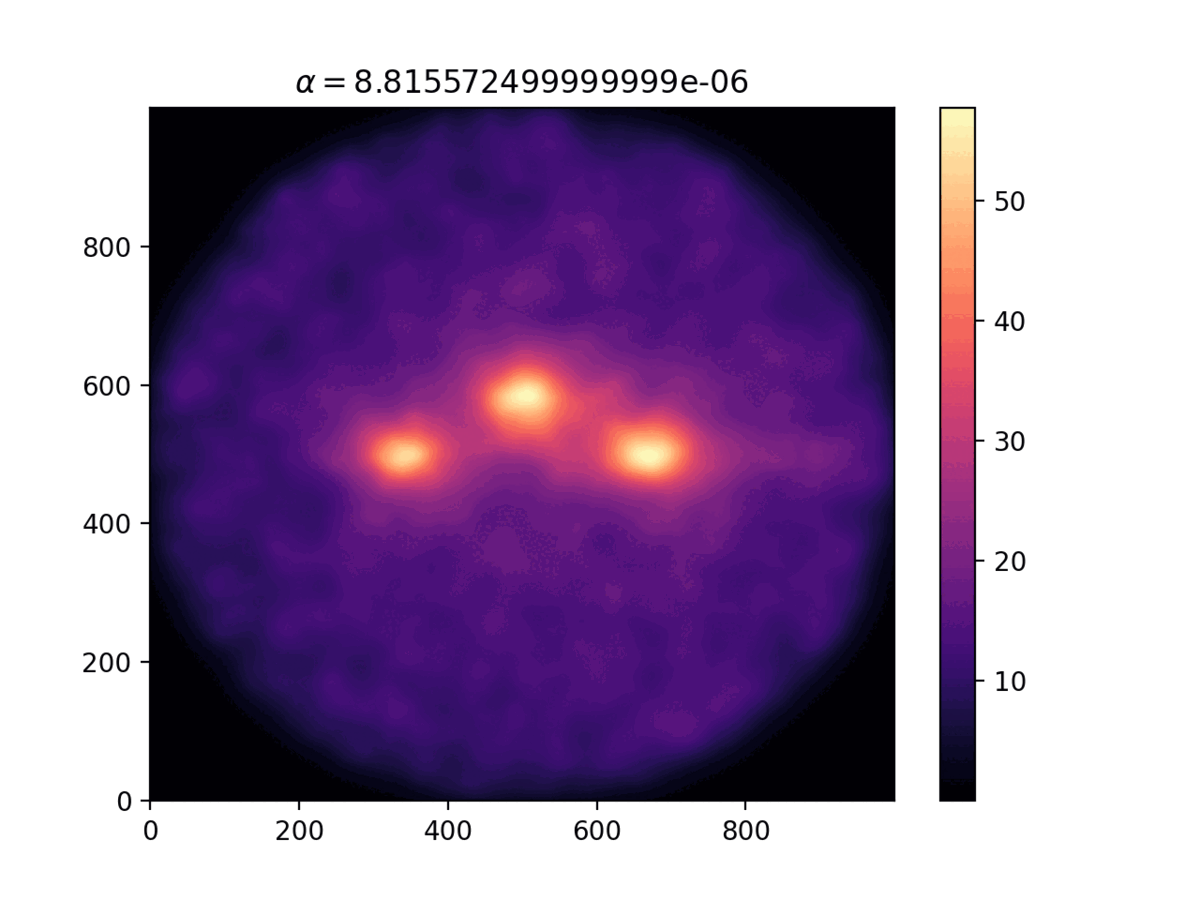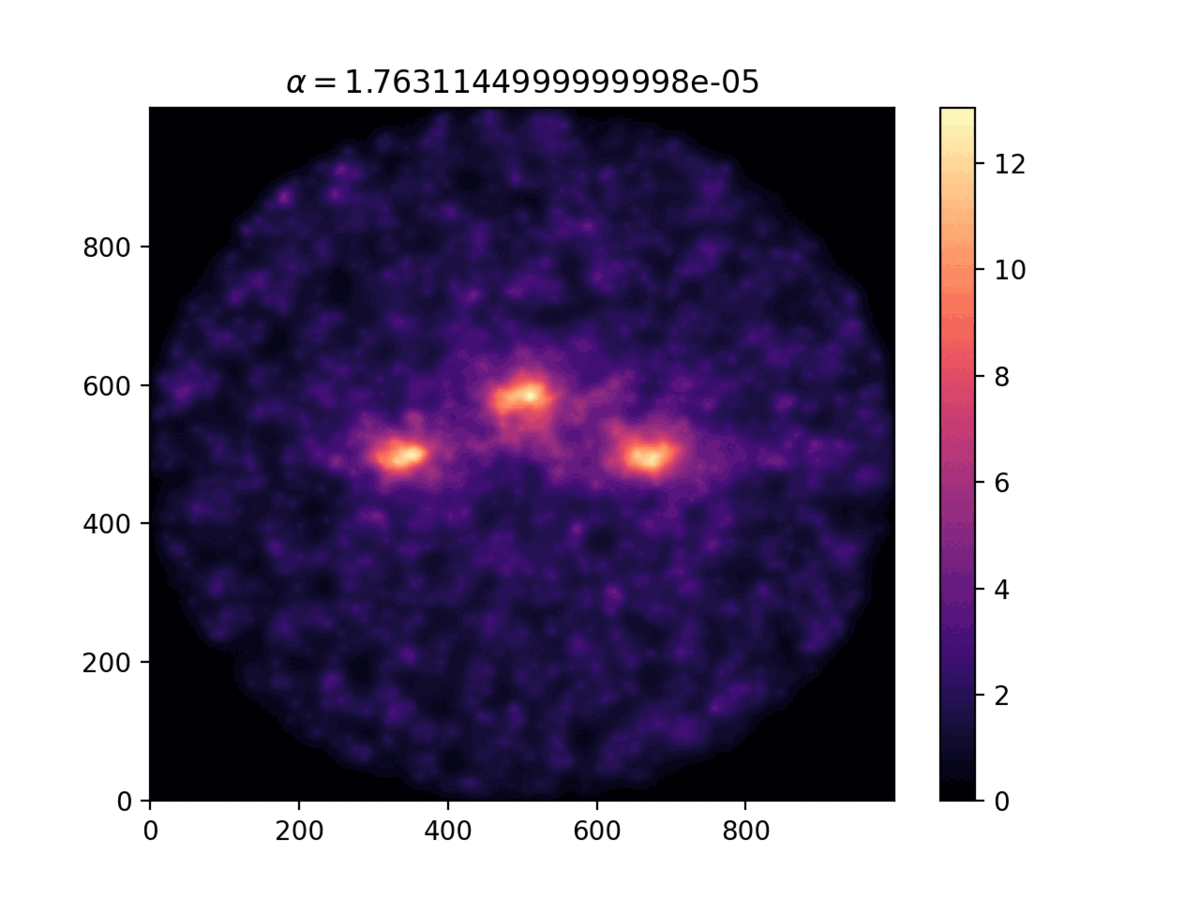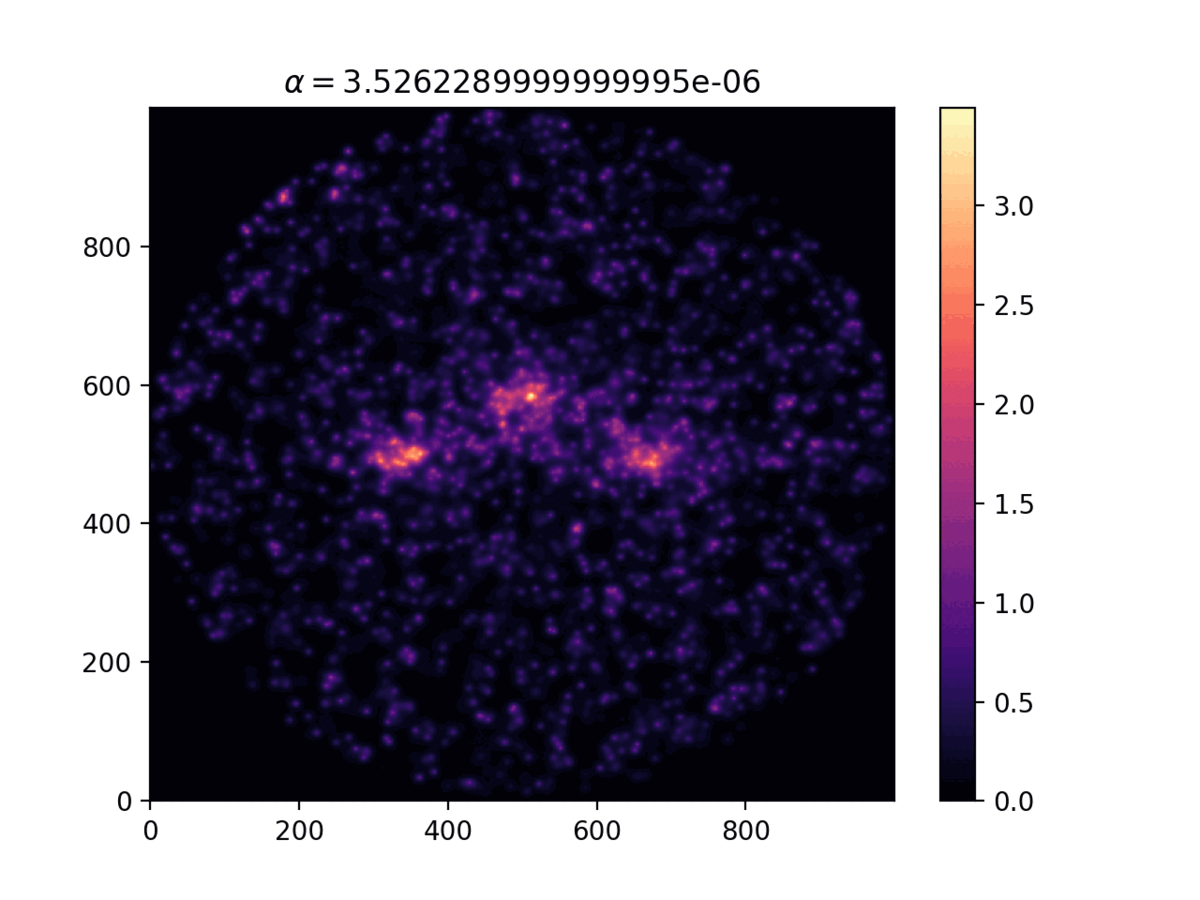 Comparison of the density distribution for different values
of the $\alpha$ parameter.
Comparison of the density distribution for different values
of the $\alpha$ parameter.
Density formula:
$$\rho_{ij} = \sum_{k = 0}^M \rho_k e^{-\alpha \sqrt{ (x_{ij} - x_k)^2 + (y_{ij} - y_k)^2 + (z_{ij} - z_k)^2}}$$
$\rho_k, x_k, y_k, z_k$ --- input data particles density and coordinates
$M = 65536$ --- number of particles in input data.
$x_{ij} = -R + 2R \frac{i}{n_x - 1}$
$y_{ij} = 0$
$z_{ij} = -R + 2R \frac{j}{n_z - 1}$
MPI Implementation
Code
Inside main:
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
// Size of total grid
int n = n_arr[k];
// Size of partial grid for each proccess
int pn = n / size;
if (n % size != 0)
pn++;
double *grid, *partial_grid;
grid = new double [pn * size * n];
partial_grid = new double [pn * n];
for (int p = 0; p < 4; p++) {
double alpha = alpha_arr[p];
gettimeofday(&t1, 0);
get_grid(grid, partial_grid, data, pn, n, alpha);
gettimeofday(&t2, 0);
if (rank == 0) {
time = (1.0e6 * (t2.tv_sec - t1.tv_sec) +
t2.tv_usec - t1.tv_usec) / 1000.0;
cout << n << " " << time << endl;
print_output(grid, n, p);
}
}
delete [] grid;
delete [] partial_grid;
}
Function 'get_grid':
void get_grid(double *grid, double *partial_grid, double *data,
int pn, int n, double alpha) {
int rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
for (int i = 0; i < pn; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
partial_grid[i * n + j] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pn; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
double xij = get_coord((double)(i + rank * pn),
(double)n);
double zij = get_coord((double)j, (double)n);
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
double x = data[k * 4 + 0];
double y = data[k * 4 + 1];
double z = data[k * 4 + 2];
double density = data[k * 4 + 3];
partial_grid[i * n + j] += density * exp(-alpha *
sqrt((x - xij) * (x - xij) +
(z - zij) * (z - zij) +
(y - 0) * (y - 0)));
}
}
}
MPI_Gather(partial_grid, pn * n, MPI_DOUBLE, grid, pn * n,
MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
Time Analysis
$$T_{paral}(P, N) = T_{arithm}(N, P) + T_{comm}(N, P)$$
$$T_{arithm}(N, P) = N \cdot \frac{N}{P} \cdot M \cdot \underbrace{\tau \cdot T}_{\text{cost of arighmetic operations inside loop}}$$
$M = 65536$ --- number of particles in input data.
$T$ --- number of arithmetic operations.
$\tau$ --- time for 1 arithmetic operation.
$$T_{comm}(N, P) = \left( \alpha + \frac{1}{\beta} \frac{N^2}{P} \right) \underbrace{\sqrt{p} }_{\text{torus}} $$
$$S(N, P) = \frac{T_{arithm}(N, P)}{T_{paral}(N, P)}$$
$$E(N, P) = \frac{S(N, P)}{P}$$
 Constants found through fitting.
Constants found through fitting.
Speedup and Efficiency
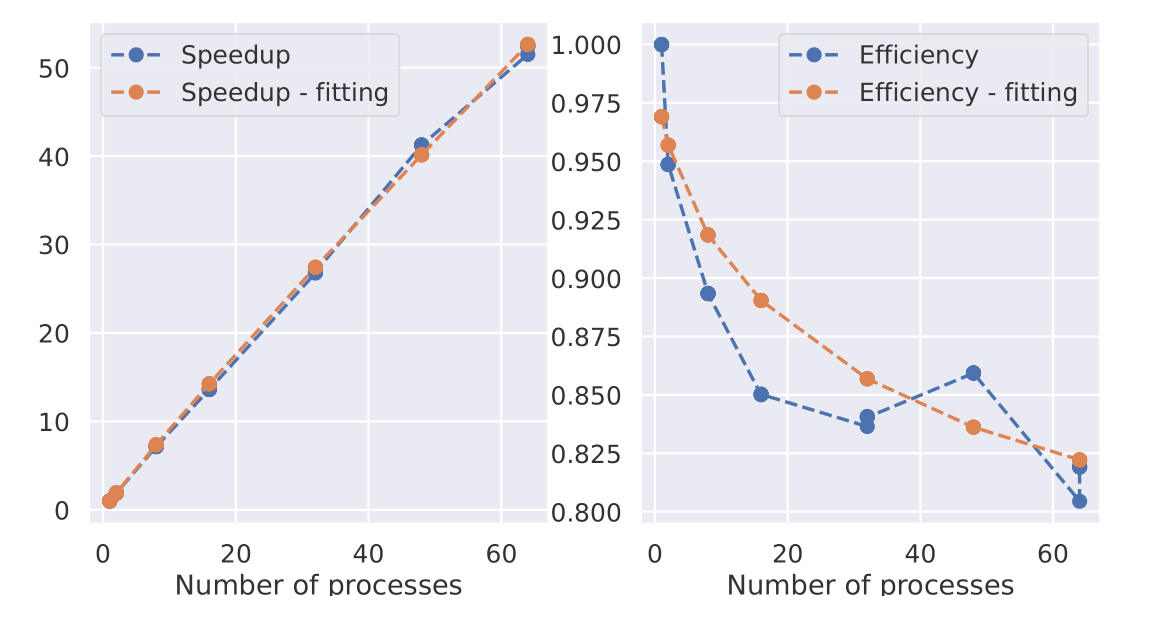 Speedup and efficiency of the MPI
implementation
Speedup and efficiency of the MPI
implementation
OpenACC Implementation
Code
#pragma acc data copyin(data[0:N*4]) copyout(grid[0:n*n])
{
#pragma acc parallel loop
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
#pragma acc loop
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
double xij = -R + (double)i / (double)(n - 1) * 2 * R;
double zij = -R + (double)j / (double)(n - 1) * 2 * R;
double cell_ij = 0;
#pragma acc loop reduction(+:cell_ij)
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
double x = data[k * 4 + 0];
double y = data[k * 4 + 1];
double z = data[k * 4 + 2];
double density = data[k * 4 + 3];
cell_ij += density * exp(-alpha *
sqrt((x - xij) * (x - xij) +
(z - zij) * (z - zij) +
(y - 0) * (y - 0)));
}
grid[i * n + j] = cell_ij;
}
}
}
Compiling: Unified Memory
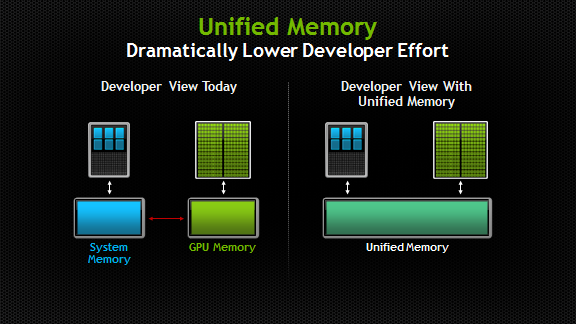
pgc++ -lstdc++ -O2 -Wall -std=c++11 -acc -ta=nvidia:managed -Minfo=accel
The 'managed' option lets us use Unified Memory.
Unified Memory creates a pool of managed memory that is shared between the CPU and GPU, bridging the CPU-GPU divide. Managed memory is accessible to both the CPU and GPU using a single pointer. The key is that the system automatically migrates data allocated in Unified Memory between host and device so that it looks like CPU memory to code running on the CPU, and like GPU memory to code running on the GPU.
Time Metrics and Comparison between MPI and OpenACC Implementations
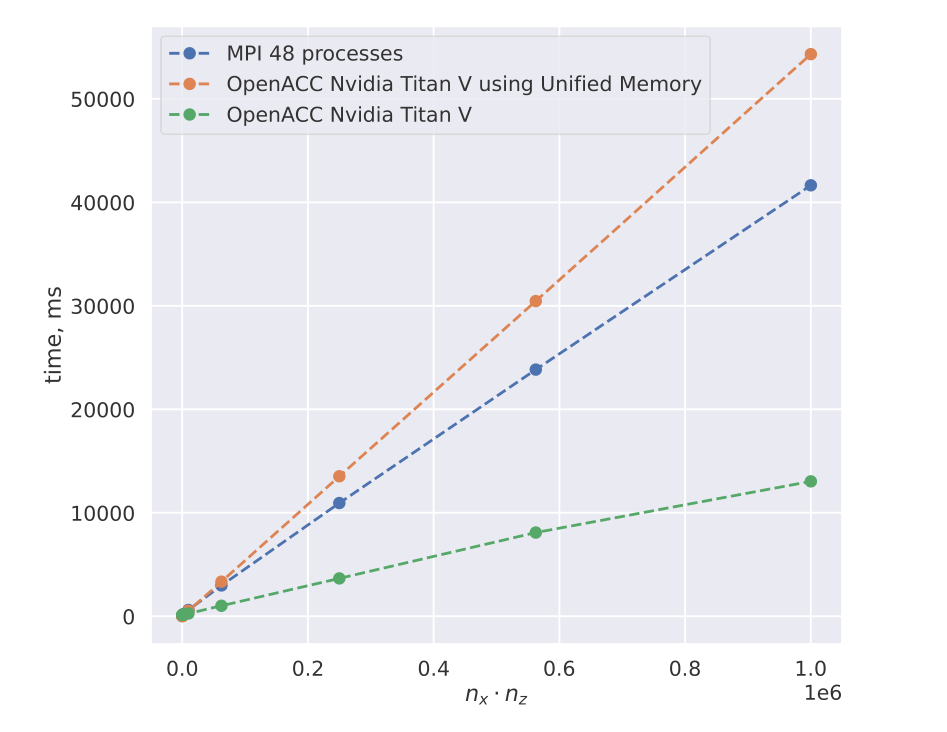 Dependence of the run time at maximum optimization for different
values of $n_x \cdot n_z$ for MPI and OpenACC
implementation.
Dependence of the run time at maximum optimization for different
values of $n_x \cdot n_z$ for MPI and OpenACC
implementation.
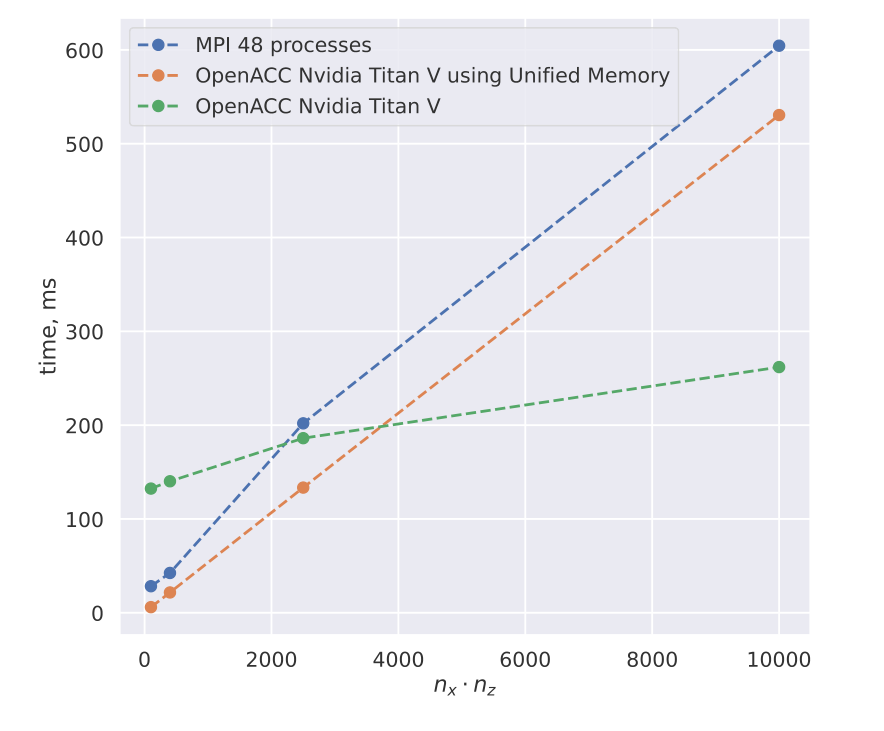 Dependence of the run time at maximum optimization for small values of
$n_x \cdot n_z$ for MPI and OpenACC
implementation.
Dependence of the run time at maximum optimization for small values of
$n_x \cdot n_z$ for MPI and OpenACC
implementation.